
Key Takeaways
- Men typically begin experiencing a gradual decline in sex drive around age 30-40, with testosterone levels dropping 1-2% annually after age 30
- The decline is usually gradual and varies significantly between individuals - sudden libido loss may indicate underlying health issues
- Multiple factors affect male sex drive, including hormonal changes, chronic diseases, psychological stress, and lifestyle choices
- Evidence-based solutions include medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and natural supplements like deer antler velvet extract
- Professional medical evaluation is recommended for sudden or severe libido changes to identify and treat underlying causes
Understanding Male Sex Drive and Its Changes Over Time
Male libido, or sex drive, represents a complex interplay of hormonal, psychological, and physical factors that significantly impact men's overall health, relationships, and quality of life. Understanding what age men lose their sex drive has become increasingly important as men seek to maintain their sexual health throughout their lives.
This comprehensive guide explores the natural timeline of male libido changes, examining when a man's sex drive decrease and the various factors that influence this process. We'll investigate evidence-based solutions for maintaining and improving sexual function, including the potential role of natural supplements like deer antler velvet extract in supporting male sexual health.
At What Age Do Men Typically Lose Sex Drive?
Natural Age-Related Decline of Libido
Research indicates that men don't suddenly lose their sex drive at a specific age, but rather experience a gradual decline that typically begins in their 30s to 40s. According to the American Urological Association, testosterone levels—the primary hormone driving male libido—begin declining at approximately 1-2% per year after age 30¹.
The Massachusetts Male Aging Study, which followed 1,709 men aged 40-70 over nine years, found that sexual desire and frequency of sexual thoughts decreased progressively with age². However, this decline varies significantly among individuals based on:
- Overall health status and fitness level
- Genetic factors and family history
- Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and substance use
- Psychological well-being and stress levels
- Relationship quality and emotional intimacy
Distinguishing Normal Decline from Sudden Loss
It's crucial to differentiate between the expected gradual decline in libido and sudden, dramatic changes that may signal underlying health problems. Normal age-related decline occurs slowly over years or decades, while sudden libido loss within weeks or months often indicates medical conditions requiring professional attention.
The International Society for Sexual Medicine emphasizes that while some decline is normal, complete loss of sexual interest or inability to become aroused warrants medical evaluation³. This distinction helps men understand when changes represent natural aging versus potential health concerns requiring intervention.
Key Factors That Affect Loss of Sex Drive in Men
Biological and Hormonal Factors
Testosterone and Hormone Imbalances: Testosterone serves as the primary driver of male sexual desire. The Endocrine Society reports that testosterone deficiency affects approximately 4-5 million men in the United States⁴. Low testosterone (hypogonadism) can result from:
- Primary testicular disorders
- Pituitary gland dysfunction
- Hypothalamic disorders
- Age-related decline in hormone production
Chronic Diseases: Multiple chronic conditions significantly impact male libido. The Journal of Sexual Medicine published research showing that men with diabetes have 3.5 times higher risk of erectile dysfunction and reduced libido⁵. Other conditions include:
- Cardiovascular disease affects blood flow
- Obesity leads to hormonal imbalances
- Sleep apnea disrupts hormone production
- Kidney and liver disease affect metabolism
Medication Effects: Numerous medications can suppress sexual desire as a side effects. The Cleveland Clinic identifies several drug classes that commonly affect libido, including antidepressants (particularly SSRIs), blood pressure medications, antihistamines, and anti-seizure drugs⁶.
Psychological and Emotional Factors
Mental health plays a crucial role in sexual desire. Depression affects an estimated 6 million men annually in the United States, with sexual dysfunction being both a symptom and consequence of depressive disorders⁷. Key psychological factors include:
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which directly suppresses testosterone production. Anxiety, particularly performance anxiety, creates a cycle where worry about sexual performance further reduces desire and function. Relationship conflicts and lack of emotional intimacy significantly impact sexual desire, as sexual health is closely tied to relationship quality and communication.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences
Modern lifestyle factors significantly impact male sexual health:
- Alcohol consumption: While moderate alcohol may temporarily reduce inhibitions, chronic heavy drinking suppresses testosterone production and damages blood vessels essential for sexual function
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and reduces circulation, directly impacting erectile function and indirectly affecting desire
- Poor diet: Diets high in processed foods and low in nutrients contribute to obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease—all factors that reduce libido
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to poor cardiovascular health, obesity, and reduced testosterone levels
- Sleep deprivation: Poor sleep quality disrupts hormone production, particularly testosterone, which is primarily produced during sleep
How to Improve Sex Drive: Evidence-Based Strategies
Medical Treatments and Interventions
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): For men with clinically diagnosed low testosterone (typically below 300 ng/dL), testosterone replacement therapy can effectively restore libido. The American College of Physicians guidelines recommend TRT for symptomatic men with clearly low testosterone levels⁸. Treatment options include:
- Topical gels and patches
- Intramuscular injections
- Subcutaneous pellets
- Oral medications (newer formulations)
However, TRT carries potential risks including increased risk of cardiovascular events, sleep apnea worsening, and prostate health concerns, requiring careful medical supervision.
Treating Underlying Conditions: Addressing chronic diseases that contribute to low libido often improves sexual function. Studies show that effective diabetes management, blood pressure control, and treatment of sleep apnea can significantly improve sexual health outcomes⁹.
Medication Review: Working with healthcare providers to identify and potentially substitute medications that suppress libido can be highly effective. Alternative medications with fewer sexual side effects are often available.
Psychological and Behavioral Approaches
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has shown significant effectiveness in treating sexual dysfunction, particularly when psychological factors are involved. Sex therapy, either individual or couples-based, addresses communication issues, performance anxiety, and relationship dynamics that impact sexual desire.
Stress reduction techniques, including mindfulness meditation, yoga, and regular relaxation practices, can lower cortisol levels and improve sexual health. The Journal of Sexual Medicine published research showing that mindfulness-based interventions significantly improved sexual function in men¹⁰.
Lifestyle Modifications
Research consistently demonstrates that lifestyle changes can significantly improve male sexual function:
- Regular Exercise: The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly. Studies show that men who exercise regularly have 30% lower risk of erectile dysfunction¹¹
- Mediterranean Diet: Rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, this eating pattern supports cardiovascular health and hormone production
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can increase testosterone levels and improve sexual function
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining 7-9 hours of quality sleep supports healthy hormone production
- Limiting Alcohol and Eliminating Tobacco: These changes improve circulation and hormone balance
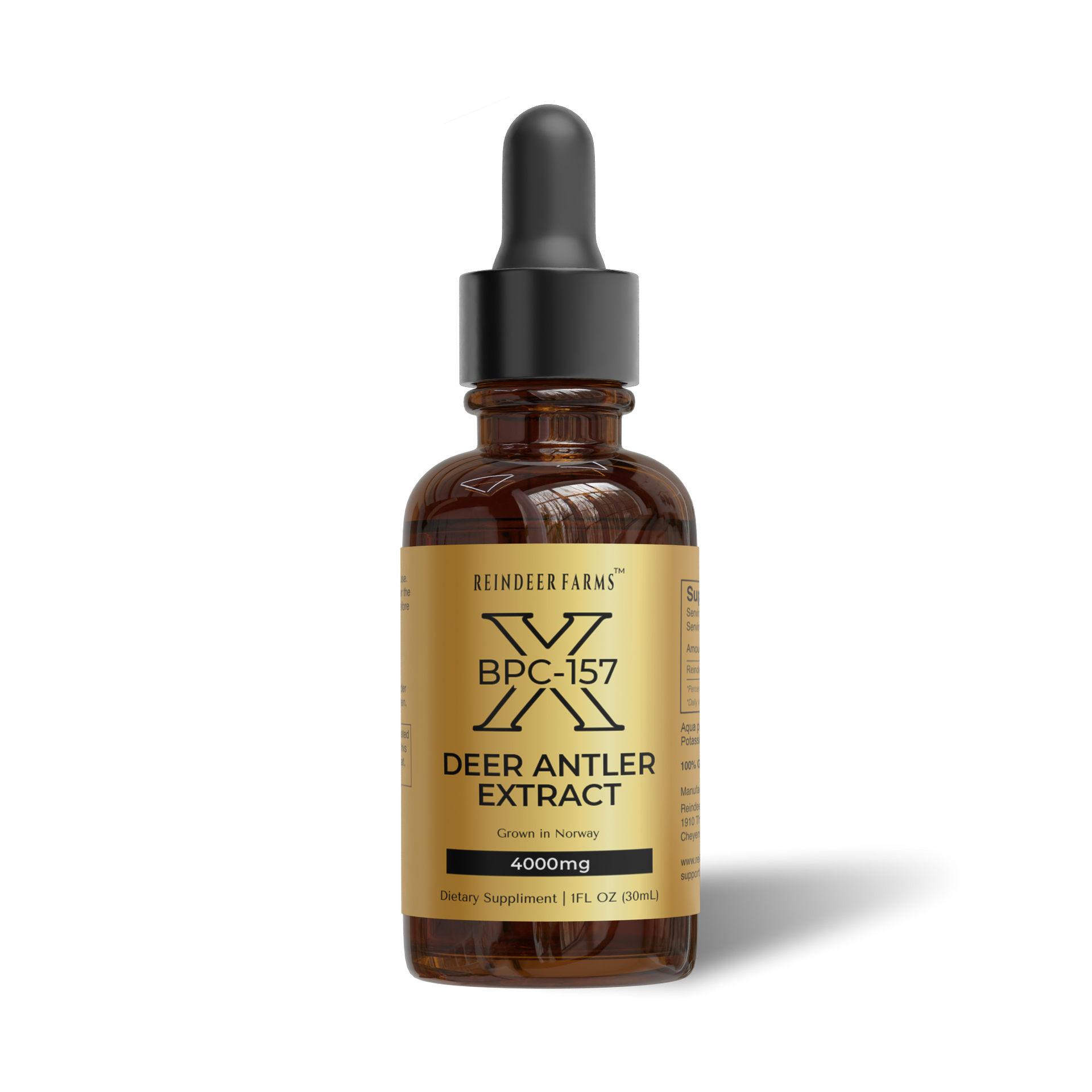
Deer Antler Velvet Extract: What Is It and How Does It Improve Sex Drive?
Overview of Deer Antler Velvet
Deer antler velvet extract is derived from the soft, cartilaginous tissue that covers growing deer antlers before they harden into bone. This substance has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for over 2,000 years to support vitality, strength, and sexual health. The velvet contains a complex array of bioactive compounds, including:
Growth factors such as insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which supports tissue growth and repair. The extract also contains essential amino acids that serve as building blocks for hormone production, along with minerals, including calcium, phosphorus, and zinc, that support reproductive health. Additionally, it provides various hormones and hormone precursors that may support the body's natural hormone production.
Scientific Evidence on Deer Antler Velvet and Male Sexual Function
While traditional use suggests benefits for male sexual health, scientific research on deer antler velvet remains limited but promising:
Animal studies have shown encouraging results, with research published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology demonstrating that deer antler velvet extract increased testosterone synthesis in animal models¹². A study in the Asian Journal of Andrology found that deer antler extract improved sexual behavior and hormone levels in male rats¹³.
Human clinical trials remain limited, though some small studies suggest potential benefits. A 2013 study published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition found that deer antler velvet supplementation improved strength and endurance in athletes, though sexual function was not directly measured¹⁴.
Research gaps include the need for larger, randomized controlled trials specifically examining sexual function outcomes in men with low libido. The optimal dosage, duration of treatment, and long-term safety profile require further investigation.
Potential Mechanisms for Libido Improvement
Deer antler velvet may support male sexual health through several mechanisms. The IGF-1 content may support testosterone production and overall reproductive health. The extract's amino acid profile provides building blocks for neurotransmitters and hormones involved in sexual desire and function.
Some research suggests deer antler velvet may improve circulation and blood flow, which is essential for sexual function. Additionally, the extract's anti-inflammatory properties may help address underlying inflammation that can interfere with hormone production and sexual health.
How Deer Antler Velvet May Complement Other Libido-Enhancing Strategies
Deer antler velvet extract may work synergistically with other evidence-based approaches to male sexual health:
When combined with regular exercise and proper nutrition, deer antler velvet may support the body's natural hormone production and recovery processes. The extract's potential circulation benefits may complement cardiovascular exercise's positive effects on sexual function.

As a natural supplement, deer antler velvet may provide an option for men seeking alternatives or complements to pharmaceutical interventions. However, it's important to note that men with hormone-sensitive conditions should exercise caution and consult healthcare providers before use.
Safety considerations include potential interactions with blood-thinning medications and the theoretical risk of affecting hormone levels in men with prostate conditions. Quality and purity of deer antler velvet products vary significantly, making source and manufacturing standards important considerations.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Certain signs and symptoms warrant professional medical evaluation:
Sudden, dramatic loss of sexual desire within a short timeframe may indicate underlying medical conditions requiring treatment. Complete inability to achieve or maintain erections, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, requires evaluation for cardiovascular or neurological conditions.
Additional concerning symptoms include persistent fatigue, mood changes, hot flashes, or loss of muscle mass, which may indicate hormonal disorders. Changes in urination patterns or pelvic pain should also prompt medical consultation.
The diagnostic process typically includes a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, hormone level testing (including total and free testosterone), and evaluation for underlying conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or sleep disorders. Healthcare providers may also assess psychological factors and medication effects.
Personalized treatment approaches consider individual health status, age, relationship factors, and personal preferences. This individualized care ensures that treatment recommendations align with each man's specific needs and circumstances.
Summary and Final Thoughts: Navigating Libido Changes Responsibly
Understanding at what age men lose their sex drive reveals that sexual health changes are a normal part of aging, typically beginning gradually in the 30s and 40s. However, the extent and impact of these changes vary significantly among individuals and can be influenced by numerous modifiable factors.
Evidence-based approaches, including medical treatment of underlying conditions, lifestyle modifications, psychological support, and potentially natural supplements like deer antler velvet extract, can help men maintain sexual health throughout their lives. While deer antler velvet shows promise based on traditional use and limited research, it should be viewed as one component of a comprehensive approach to male sexual health.
Open communication with healthcare providers ensures that concerning changes receive appropriate evaluation and treatment. Similarly, honest communication with partners about sexual health changes supports relationship quality and mutual understanding. Remember that seeking help for sexual health concerns is a sign of taking responsibility for overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can men regain lost sex drive naturally?
Yes, many men can improve their sex drive through natural approaches including regular exercise, stress reduction, improved sleep, healthy diet, and addressing underlying health conditions. However, the effectiveness depends on the underlying causes and individual circumstances.
What are the main categories of factors affecting male libido?
Male libido is influenced by three main categories: biological factors (hormones, chronic diseases, medications), psychological factors (stress, depression, anxiety, relationship quality), and lifestyle factors (diet, exercise, sleep, substance use).
How does deer antler velvet compare to testosterone therapy?
Testosterone therapy is a proven medical treatment for clinically diagnosed low testosterone, while deer antler velvet is a natural supplement with limited scientific research. Testosterone therapy requires medical supervision due to potential side effects, while deer antler velvet is generally considered safer but with less established efficacy for sexual health.
References
-
Bhasin, S., et al. (2018). Testosterone therapy in men with hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 103(5), 1715-1744.
-
Araujo, A. B., et al. (2004). Changes in sexual function in middle-aged and older men: Longitudinal data from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 52(9), 1502-1509.
-
Salonia, A., et al. (2021). European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health. European Urology, 80(2), 222-241.
-
Mulligan, T., et al. (2006). Prevalence of hypogonadism in males aged at least 45 years: The HIM study. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 60(7), 762-769.
-
Maiorino, M. I., et al. (2014). Diabetes and sexual dysfunction: Current perspectives. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity, 7, 95-105.
-
Medications that can cause erectile dysfunction. Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/10035-erectile-dysfunction
-
Depression in men. National Institute of Mental Health. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/men-and-depression
-
Qaseem, A., et al. (2014). Testosterone treatment in adult men with age-related low testosterone: A clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine, 162(8), 601-613.
-
Jackson, G., et al. (2010). Erectile dysfunction and coronary artery disease prediction: Evidence-based guidance and consensus. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 64(7), 848-857.
-
Stephenson, K. R., & Kerth, J. (2017). Effects of mindfulness-based therapies for female sexual dysfunction: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Sex Research, 54(7), 832-849.
-
Lamina, S., et al. (2009). Effects of continuous exercise training programme on sexual function among men with erectile dysfunction. International Journal of Impotence Research, 21(6), 348-355.
-
Li, C., et al. (2003). Deer antler extract improves fatigue and physical strength in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 87(1), 25-29.
-
Wang, B. X., et al. (1988). The effect of deer antler extract on sexual behavior in male rats. Asian Journal of Andrology, 10(4), 549-553.
-
Allen, M., et al. (2013). Effect of deer antler velvet on strength, power, and endurance performance. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 23(6), 615-621.


Comments (0)
Back to News