
Introduction
IGF-1, or Insulin-like Growth Factor 1, is a fascinating and multifaceted hormone that plays a crucial role in the human body. Beyond its involvement in growth and development, IGF-1 has gained significant attention in the realm of athletic performance. In this blog post, we'll explore what IGF-1 is, how it functions in the body, and its relevance for athletes seeking to maximize their potential.
Understanding IGF-1
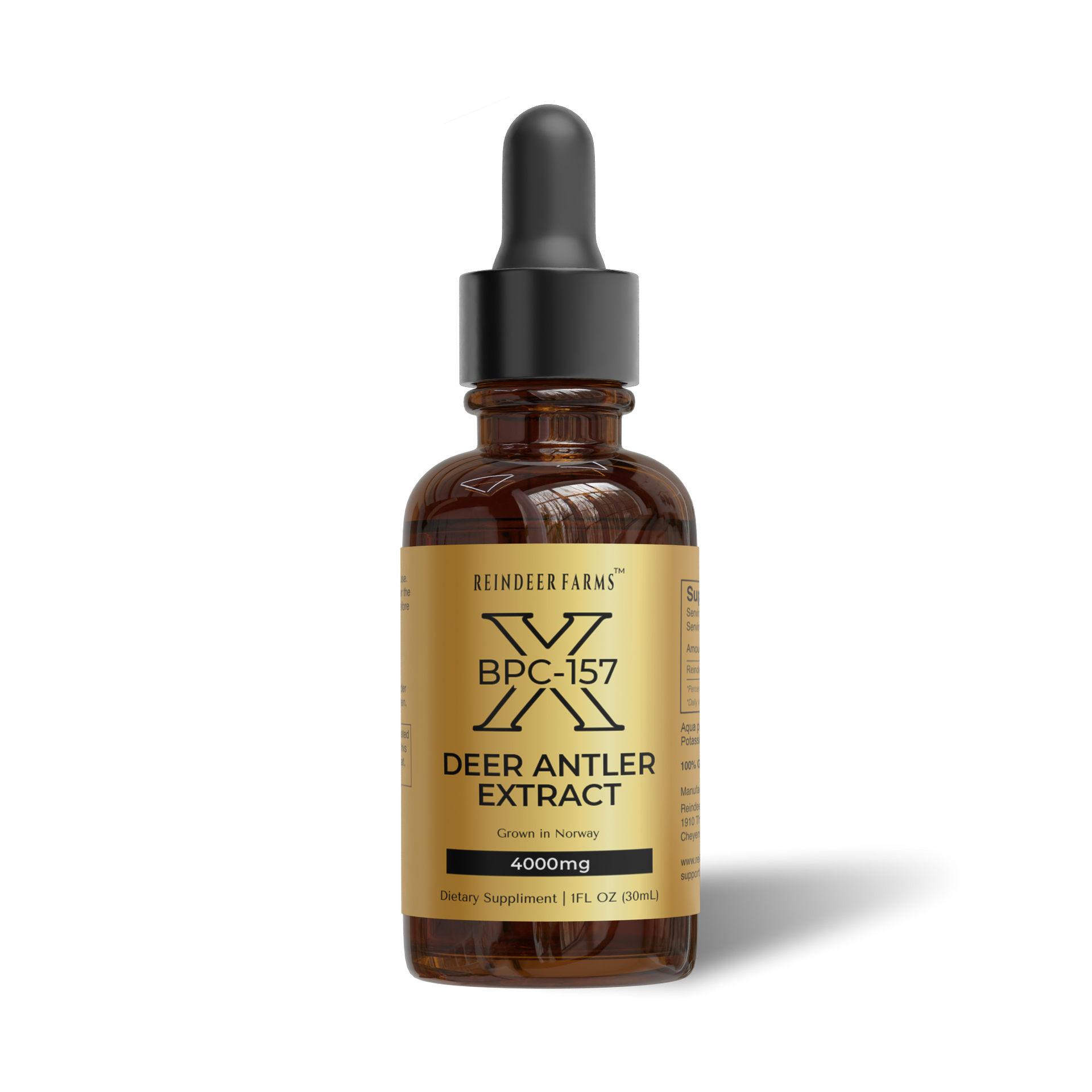
IGF-1 is a peptide hormone produced primarily by the liver, in response to the stimulation of growth hormone (GH) secretion from the pituitary gland. It belongs to the family of growth factors and is closely related to insulin, both structurally and functionally. This similarity in structure is why it's called "Insulin-like" Growth Factor.
The Role of IGF-1 in the Human Body
-
Growth and Development: IGF-1 plays a pivotal role in childhood growth and development. It stimulates the growth of bones, cartilage, and various tissues, ensuring proper physical development during adolescence.
-
Tissue Repair and Regeneration: Beyond growth, IGF-1 continues to be essential in adulthood. It aids in tissue repair and regeneration, making it crucial for maintaining muscle, connective tissue, and overall body structure.
-
Metabolism: IGF-1 also influences glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, helping to regulate blood sugar levels.
IGF-1 and Athletic Performance
Now, let's delve into how IGF-1 is relevant for athletes:
-
Muscle Growth: IGF-1 promotes muscle cell growth and differentiation, contributing to the development of lean muscle mass. For athletes, this means increased potential for muscle hypertrophy and enhanced strength.
-
Recovery and Healing: IGF-1's role in tissue repair and regeneration is invaluable for athletes recovering from injuries or strenuous workouts. Faster recovery means more frequent and productive training sessions.
-
Reduced Muscle Loss: IGF-1 can help prevent muscle wasting (atrophy) during periods of inactivity or calorie restriction, aiding athletes in maintaining their hard-earned gains.
-
Improved Endurance: Some studies suggest that IGF-1 may enhance endurance by promoting the efficient use of energy and oxygen in muscle tissue.
-
Enhanced Athletic Performance: The cumulative effects of increased muscle mass, faster recovery, and reduced muscle loss can lead to overall improved athletic performance, whether in strength sports, endurance events, or other athletic endeavors.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
It's important to note that the use of exogenous IGF-1, such as synthetic supplements, is considered unethical and illegal in most sports. Athletes should aim to naturally optimize their IGF-1 levels through healthy nutrition, sufficient sleep, and effective training protocols. Furthermore, doping regulations in sports organizations strictly prohibit the use of IGF-1 and other performance-enhancing substances.
Conclusion
IGF-1 is a remarkable hormone with diverse functions in the human body, including its significance for athletes. While it offers potential benefits in terms of muscle growth, recovery, and performance, athletes must prioritize natural and ethical means of enhancing IGF-1 levels. Achieving athletic excellence is not solely about maximizing hormones but also about adhering to the principles of fair play, integrity, and sportsmanship.


Comments (0)
Back to News